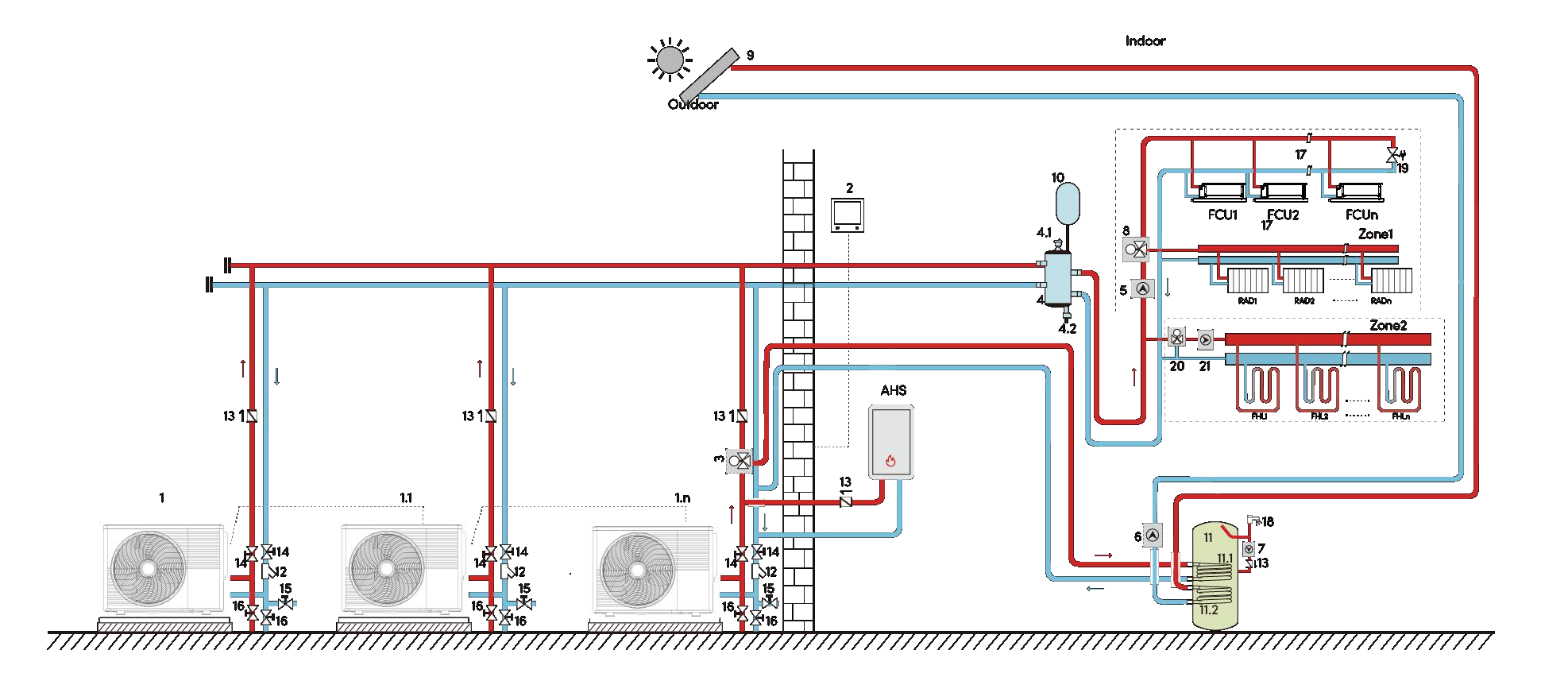
What is Air Source Heat Pump Cascade Systems?
As the demand for efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions grows, air source heat pumps have emerged as a reliable alternative for residential and commercial spaces.
Heat pumps have been gaining popularity as an efficient and versatile heating and cooling technology in recent years. With their ability to provide both heating and cooling functions, heat pumps offer a compelling solution for homeowners looking to enhance their indoor comfort while minimizing energy consumption. In this article, we will explore the important topic of electricity usage in heat pumps and how various factors can influence their energy efficiency. Understanding the electricity usage of heat pumps is crucial for homeowners who want to make informed decisions about their HVAC systems and manage their energy consumption effectively.

Several factors play a role in determining the electricity usage of heat pumps. By understanding these factors, homeowners can make informed choices when it comes to selecting, operating, and optimizing their heat pump systems. Here are the key factors that influence electricity usage:
Size: The size of a heat pump system is determined by the heating and cooling requirements of the space it serves. An oversized heat pump may cycle on and off more frequently, leading to inefficient energy usage. Conversely, an undersized heat pump may struggle to meet the desired temperature, leading to prolonged operation and higher energy consumption.
Efficiency: The efficiency of a heat pump is measured by its Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) for heating. Higher SEER and HSPF ratings indicate greater energy efficiency, meaning the heat pump can produce more heating or cooling output per unit of electricity consumed.
Local Climate: The climate in which a heat pump operates can impact its electricity usage. Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient in moderate climates, where the temperature extremes are not too severe. In colder climates, heat pumps may rely on auxiliary heating elements or defrost cycles, which can increase electricity usage.
Indoor Temperature: The desired indoor temperature set on the thermostat affects the frequency and duration of heat pump operation. Higher temperature settings in heating mode or lower temperature settings in cooling mode will result in longer run times and potentially higher electricity usage.
Home Insulation: The level of insulation in a home significantly impacts the efficiency of a heat pump system. Well-insulated homes retain conditioned air better, allowing heat pumps to operate more efficiently and reducing the overall electricity usage.
By considering these factors and making informed choices, homeowners can optimize the electricity usage of their heat pump systems, thereby achieving greater energy efficiency and cost savings. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the average electricity consumption of heat pumps, the monthly costs associated with their operation, and strategies for optimizing electricity usage and reducing energy bills.
Shenling will be the best solution of how to use a heat pump in winter
Heat pumps are renowned for their energy efficiency, making them a more sustainable option compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. By harnessing the ambient heat from the surrounding environment, heat pumps can produce a substantial amount of heating or cooling without relying solely on electricity consumption. Here are some key points to consider regarding the electricity usage of heat pumps:
Energy Efficiency Comparison: Heat pumps outperform conventional heating and cooling systems in terms of energy efficiency. While electric furnaces or baseboard heaters convert all electricity into heat, heat pumps utilize a small amount of electricity to transfer heat from one place to another. This energy transfer process enables heat pumps to achieve high efficiency and reduce overall electricity usage.
Average Electricity Consumption: The actual electricity consumption of a heat pump depends on various factors, including the size and efficiency of the system, climate conditions, and user settings. On average, a heat pump can consume between 500 kilowatt-hours (kWh) to 1,500 kWh per month. However, it’s important to note that these figures are estimates and can vary depending on individual circumstances.
Determining the exact monthly electricity usage of a heat pump requires consideration of specific factors such as system size, usage patterns, and climate. However, by estimating the average range mentioned above, homeowners can calculate the monthly cost based on their local electricity rates. For example, if the heat pump consumes 800 kWh per month and the electricity rate is $0.12 per kWh, the monthly cost would be $96 (800 kWh x $0.12).
On a daily basis, a heat pump typically consumes an average of 16 kWh to 50 kWh, depending on the factors mentioned earlier. However, it’s essential to note that energy efficiency plays a crucial role in reducing electricity usage. Heat pumps with higher efficiency ratings, represented by a higher Coefficient of Performance (COP), can produce more heating or cooling output per unit of electricity consumed.
By understanding the electricity consumption patterns of heat pumps and their energy efficiency, homeowners can make informed decisions about system operation, optimize energy usage, and potentially reduce their monthly electricity bills. In the following sections, we will explore strategies for optimizing electricity usage, maintaining energy efficiency, and achieving cost savings with heat pump systems.
The average daily electricity consumption of a heat pump varies depending on factors such as system size, efficiency, climate conditions, and user settings. On average, heat pumps consume between 16 kilowatt-hours (kWh) to 50 kWh per day. It’s important to note that these numbers are estimates and can fluctuate based on individual circumstances. However, understanding the daily electricity consumption helps homeowners gauge their energy usage and make informed decisions about optimizing their heat pump systems.
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a key metric that indicates the energy efficiency of a heat pump. It represents the ratio of the heat output to the electricity input. For example, a heat pump with a COP of 3 produces three units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. The higher the COP, the more energy-efficient the heat pump is, meaning it can provide more heating or cooling output using less electricity. Energy-efficient heat pumps with higher COP ratings are ideal for reducing electricity usage and achieving cost savings.
Proper Heat Pump Sizing and Professional Installation: It is crucial to ensure that the heat pump is properly sized for the specific heating and cooling requirements of the space. Undersized or oversized heat pumps can lead to inefficient operation and increased electricity usage. Consulting with a professional HVAC contractor can help determine the appropriate size and ensure proper installation, maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing electricity consumption.
Regular Maintenance and Upkeep: Conducting routine maintenance tasks can optimize the performance of a heat pump and reduce energy consumption. Some maintenance tips include:
When comparing heat pump electricity usage to other heating and cooling methods, heat pumps generally offer significant cost savings. Heat pumps can save, on average, 30% to 50% on monthly electricity bills compared to electric furnaces or traditional air conditioning units. The exact savings will depend on factors such as local electricity rates, climate conditions, and the efficiency of the heat pump system. By opting for a heat pump, homeowners can reduce electricity usage, decrease their carbon footprint, and potentially enjoy substantial cost savings in the long run.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve deeper into other aspects of heat pump electricity usage, including monthly costs, energy efficiency ratings, and considerations for selecting the right heat pump for your needs.
When comparing heat pump electricity usage to other heating and cooling methods, heat pumps offer significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and cost savings. Let’s take a closer look at how heat pumps stack up against traditional systems:
Electric Furnaces: Electric furnaces convert all the electricity they consume into heat, resulting in high electricity usage. In contrast, heat pumps transfer heat from the outside air or ground, requiring less electricity to produce the same amount of heating. This makes heat pumps much more energy-efficient and cost-effective for heating purposes.
Gas or Oil Furnaces: While gas or oil furnaces can provide effective heating, they rely on the combustion of fossil fuels, which can be less efficient and more expensive compared to heat pumps. Heat pumps utilize electricity for heat transfer rather than burning fuel, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact.
Air Conditioners: Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling functions, making them more versatile than standalone air conditioners. When operating in cooling mode, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from inside the home to the outside, similar to how they work in heating mode. Although the electricity consumption may be slightly higher during cooling, the overall energy efficiency of heat pumps still makes them a more efficient option compared to separate heating and cooling systems.
Heat pumps offer the potential for significant cost savings compared to other heating and cooling methods. The exact savings will vary depending on factors such as electricity rates, climate conditions, and the efficiency of the heat pump system. However, studies have shown that homeowners can save, on average, 30% to 50% on monthly energy bills by using heat pumps instead of electric furnaces or traditional air conditioning units. These savings can add up over time and contribute to a more sustainable and budget-friendly home.
Heat pumps have gained popularity as a highly efficient and cost-effective solution for heating and cooling needs. By utilizing electricity for heat transfer rather than solely relying on electric resistance or fossil fuel combustion, heat pumps offer remarkable energy efficiency. This efficiency, combined with their versatility in providing both heating and cooling functions, makes heat pumps an attractive option for homeowners seeking to reduce electricity usage and lower their energy costs.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the factors that influence heat pump electricity usage, such as size, efficiency, climate, and user settings. We’ve also discussed the importance of proper installation, regular maintenance, and the benefits of heat pump energy efficiency ratings like the Coefficient of Performance (COP). By understanding and optimizing these factors, homeowners can maximize the energy efficiency of their heat pump systems, reduce their carbon footprint, and potentially enjoy significant cost savings over time.
When considering heating and cooling options for your home, it’s clear that heat pumps offer an environmentally friendly and economically viable solution. By harnessing the natural heat from the environment, heat pumps not only provide reliable comfort but also contribute to a sustainable future.

As the demand for efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions grows, air source heat pumps have emerged as a reliable alternative for residential and commercial spaces.

On December 5th, 2023, the signing ceremony for the ‘Shenling Special Air Conditioning and Ventilation Equipment Manufacturing (Gaozhou) Project’ took place in Gaozhou, Maoming. Notable

Embracing the Sustainable Future with R290 Heat Pumps In recent years, the quest for sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions has led to significant advancements in